To understand the basic knowledge of an elbow, the determination of an elbow must know the diameter, radius, and angle of the elbow, and some have a straight section. According to the angle, there are 45 degree pipe elbow, 90 ° and 180 °, which are the most commonly used, and other abnormal angle bends, such as 60°, are also included according to the engineering needs. The angle of the elbow needs to be measured with a tool, and only 180 degrees, 90 degrees, and 45 degrees can be seen.
Jianzhi offers a wide selection of pipe fittings, including the 3/4 street 90, short radius elbow, 90 degree elbow pipe, 90 degree elbow conduit, 1 2 90, and 6 inch 90 degree elbow. These high-quality fittings are essential for creating precise angles and bends in piping systems, ensuring efficient flow and easy installation. Whether you need a tight short radius elbow for space-constrained applications or a larger 6 inch 90 degree elbow for industrial systems, Jianzhi provides reliable and durable solutions to meet the specific requirements of any project. Jianzhi offers a comprehensive selection of 90 fittings, designed to facilitate seamless changes in direction within piping systems. These fittings are crafted from high-quality malleable iron and undergo a rigorous manufacturing process to ensure durability and reliability. Ideal for both residential and industrial applications, Jianzhi 90 fittings provide optimal flow characteristics and are easy to install, making them a practical choice for any plumbing or heating project. With a commitment to quality and customer satisfaction, Jianzhi continues to be a trusted supplier for all your fitting needs.

Formula for calculating the size of the elbow:
- 1. 5 times the center height of the elbow = path * 1.524, in fact, is the path * multiple, the number after the decimal point of the resulting result is round to the nearest integer, such as the path of 219 is 200. The center height is 200 ≤ 1.524 ≤ 304.8, take 305; if the path of 114 is 100, the center height is 100 ≤ 1.524 ≤ 152.4, take 152.
(suitable for DN100 and above elbow curvature radius algorithm for convenient and fast calculation). - Stamp height = center height + radius of elbow, such as 1.5 times diameter 219 elbow height = 305 x 219 ≤ 2 ≤ 305 ≤ 109.5 ≤ 414.5.
- The outer arc length = (center height + radius) * 3.14 ≤ 2 ≤ 360 * degrees, that is, (stamp height) * 3.14 ≤ 2 ≤ 360 * degrees, from which the outer arc length of 90 degree fitting elbow can be calculated = poke height * 3.14 × 2.
- Inner arc length = (center height-radius) * 3.14 ≤ 2 ≤ 360 * degrees.
- The blanking length of the elbow = the height of the center of the elbow * 3.14 ≤ 2 * the outer diameter of the elbow / pipe diameter + (pipe wall thickness * 3) + machining allowance, such as using 180 × 8 pipe blanking, pushing 273 elbow, the above formula can be calculated:
The blanking length is 381 ≤ 1.57 ≤ 273 / 180 / 24 / 931.22 mm + processing allowance.
Calculation Formula for a 45-Degree Elbow in a Pipeline
- The calculation method for the short pipe in the middle of two 45 degree bends is as follows: short connection length = height difference x 1.4142 ≤ 0.8284R, R = bending radius of elbow (that is, the length of a 90 elbow fitting bending head).
- First of all, calculate the center height. Then the central length minus the height of the elbow on both sides is the short pipe length in the middle.
The elbow requires the radius of curvature to be controlled. For example, if the radius length is 1.5D, the curvature radius must be within the required tolerance range. Because most of these pipe fittings are used for welding, in order to improve the welding quality, the end of the car must be inserted into a groove, leaving a certain angle, with a certain edge. This requirement is also relatively strict, depending on how thick the edge is, how much angle and deviation range are specified, and the geometric of the pipe fittings.
Formula for calculating center to end distance of such elbows is as follows:
For standard degrees of pipe elbows such as 45° and 90°, elbow center to end dimensions are available in standard pipe charts. But many times, custom elbow angles are required at site which should be cut from standard 45° or 90° elbows.
Elbow length in mm = Tan(Elbow Angle/2) X Elbow Radius in mm
Where:
The center to end dimension for 90° Long Radius elbows, as listed in ASME B16.9 dimension tables, is equal to the elbow’s radius. Tan(90/2) i.e. Tan 45 is 1, which is why.
Typically, 90 degree standard elbows are used to cut custom elbow angles between 45 and 90 degrees. However, elbows with custom angles less than 45 degrees are typically cut from the 45 degree standard elbow. To find the elbow radius for a conventional 45-degree elbow, divide the center-to-end measurement given in the dimension tables by Tan (22.5). The elbow angle for custom degrees can then be obtained using the aforementioned formula.
Same procedure applies to 3D elbows.
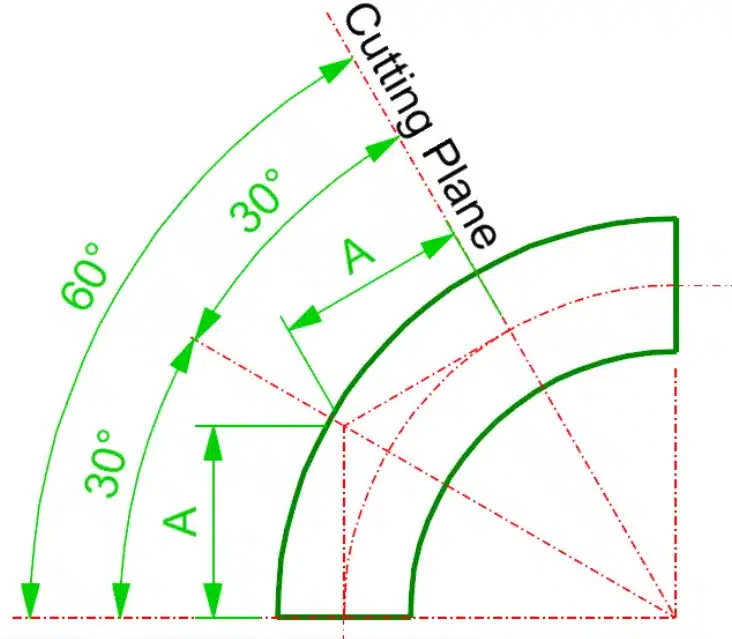
Technical specifications needed to make elbows:
Controlling the radius of curvature is necessary. For instance, the radius of curvature needs to fall within the necessary tolerance if the radius is 1.5D. Since the majority of these fittings are used for welding, the ends are car-grooved to leave a specific angle and edge. This requirement is more stringent since the edge must be thick, the angle must be determined, and the deviation range must be observed. Certain provisions have far larger geometric measurements than fittings. The elbow’s mechanical characteristics and surface quality are essentially the same as those of the tubes. The pipe that needs to be joined has the same steel material for ease of welding.
For example, if the elbow dimensions are 10 inches by 90 degrees, the path D is 250 and the center height is 250 * 1.524 = 381. The algorithm for calculating the radius of curvature of DN100 and above is quick and simple to use.
1.1.5 times the center of the elbow height A = diameter * 1.524; in fact, the path diameter D * multiples. The decimal number of the result will be rounded to the nearest integer number.
2.Poke height is equal to the center height plus the elbow’s radius; for example, a 10-inch, 90-degree elbow with a 273-diameter would have 305+273/2=441.5 in Poke height.
3.The outer arc length of the 90 degree elbow can be computed as follows: stamp High *3.14/2. The outside arc length of the elbow is equal to (center height + radius) * 3.14 * 2/360 * degrees, or (poke height) * 3.14 * 2/360 * degrees.
4.(Central height – radius) * 3.14 * 2/360 * degrees is the length of the inner arc.
The theoretical weight of the elbow
Weight of elbow = (outer diameter-wall thickness) * wall thickness * 0.02466 * length.
1) The outer diameter is not equal to the nominal diameter, equal to the outer diameter at the groove of series 2.
2) length = 2 π R * angle / 360, the calculated weight length of the elbow is the arc length corresponding to the angle of the elbow in the circumference of R as the radius.
3) R is the bending radius of the elbow.
AUTHORS:Jianzhi pipe fitting
Specialist Malleable Iron Fittings Manufacturer – Jianzhi pipe fittings
galvanized pipe fittings catalog
Formula for Calculating the Size of Elbow in Piping Systems
In piping system design and fabrication, accurately calculating the size of an elbow fitting is essential for ensuring proper alignment, smooth fluid flow, and efficient installation. Elbows are used to change the direction of pipelines, and their dimensions directly affect pressure loss, material consumption, and system reliability.
This technical guide explains the core formulas used to calculate elbow dimensions, including center-to-end distance, arc length, bend radius, and blank length. These calculations are widely applied in oil and gas, chemical processing, water supply, HVAC, and industrial pipeline projects.
Key Geometric Parameters of an Elbow
Before applying any formula, it is important to understand the basic parameters that define an elbow:
Nominal Diameter (D)
The inside diameter of the pipe connected to the elbow.
Bend Radius (R)
The distance from the center of curvature to the centerline of the pipe.
Elbow Angle (θ)
The change in direction, commonly 45°, 90°, or 180°.
Wall Thickness (t)
The thickness of the pipe wall, which affects blank length and forming allowance.
Center-to-End Distance Calculation
The center-to-end distance (C) is one of the most important dimensions for elbow installation. For long radius elbows (LR), the standard formula is:
C = 1.5 × D
This means the center of curvature is 1.5 times the pipe diameter from each end of the elbow. Long radius elbows are preferred in most industrial systems because they reduce flow resistance and pressure loss.
For short radius elbows (SR):
C = 1.0 × D
Arc Length Formula of an Elbow
The arc length represents the curved length of the elbow centerline.
Arc Length (L) = π × R × θ / 180
- Where:
- R = bend radius
- θ = elbow angle in degrees
This formula is widely used in fabrication planning and CNC bending machines.
External and Internal Arc Length
Because an elbow has wall thickness, the external and internal arc lengths are different.
- External Arc = (R + t) × π × θ / 180
- Internal Arc = (R – t) × π × θ / 180
These values are important when calculating material deformation during hot bending or cold forming.
Blank Length Calculation for Elbow Fabrication
The blank length refers to the length of straight pipe needed to manufacture an elbow.
A commonly used practical formula is:
Blank Length = R × π × θ / 180 + (3 × t) + machining allowance
This allows engineers to estimate raw material requirements accurately.
Elbow Offset Formula for Custom Angles
For non-standard angles, the take-off length can be calculated using:
Take-off = R × tan(θ / 2)
This is especially useful in site installation when calculating pipe offsets and spatial layouts.
Standard Elbow Dimension Reference Table
| Elbow Type | Angle | Radius Type | Center-to-End (C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LR Elbow | 45° | 1.5D | 1.5D × 0.707 |
| LR Elbow | 90° | 1.5D | 1.5D |
| LR Elbow | 180° | 1.5D | 3.0D |
| SR Elbow | 90° | 1.0D | 1.0D |
| SR Elbow | 180° | 1.0D | 2.0D |
This table follows common ASME B16.9 dimensional principles used in industrial fittings.
Typical Engineering Application Table
| Parameter | Symbol | Engineering Use |
|---|---|---|
| Nominal diameter | D | Pipe size matching |
| Bend radius | R | Flow resistance control |
| Elbow angle | θ | Direction change |
| Wall thickness | t | Structural strength |
| Center-to-end | C | Installation spacing |
| Arc length | L | Fabrication length |
Why Accurate Elbow Calculation Matters
Accurate elbow dimension calculation directly affects:
- Pressure drop and flow efficiency
- Material cost and fabrication waste
- Installation accuracy and alignment
- Stress distribution in piping systems
- Compliance with engineering standards
In high-pressure systems such as oil & gas or chemical plants, incorrect elbow dimensions may cause excessive turbulence, erosion, or even structural failure.
Practical Use in Piping Design
In real-world engineering projects, elbow calculations are used for:
- Isometric piping drawings
- BOM (Bill of Materials) preparation
- CNC pipe bending programs
- Welding layout and fitting alignment
- 3D piping system modeling
Most professional engineers combine formula-based calculations with standardized dimension tables to ensure both accuracy and compliance.
Conclusion
The formula for calculating the size of an elbow is a fundamental part of piping engineering. By understanding center-to-end distance, arc length, bend radius, and blank length, engineers can design efficient and reliable pipeline systems.
Combining mathematical formulas with industry standards such as ASME ensures precision, reduces material waste, and improves overall system performance. Whether for fabrication, installation, or system design, accurate elbow sizing is essential for any professional piping project.
