Product Description
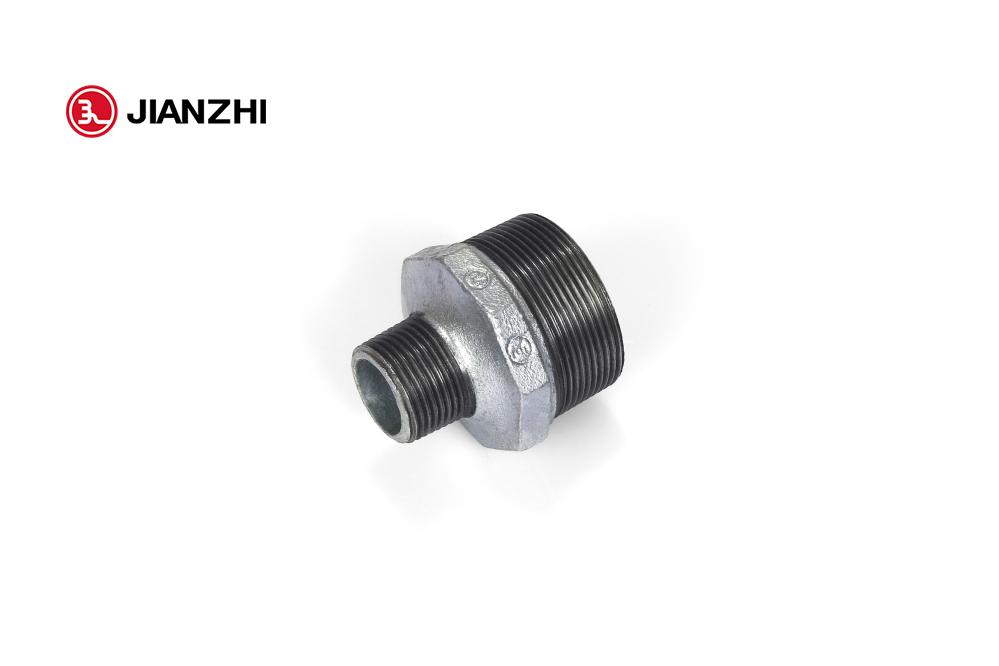
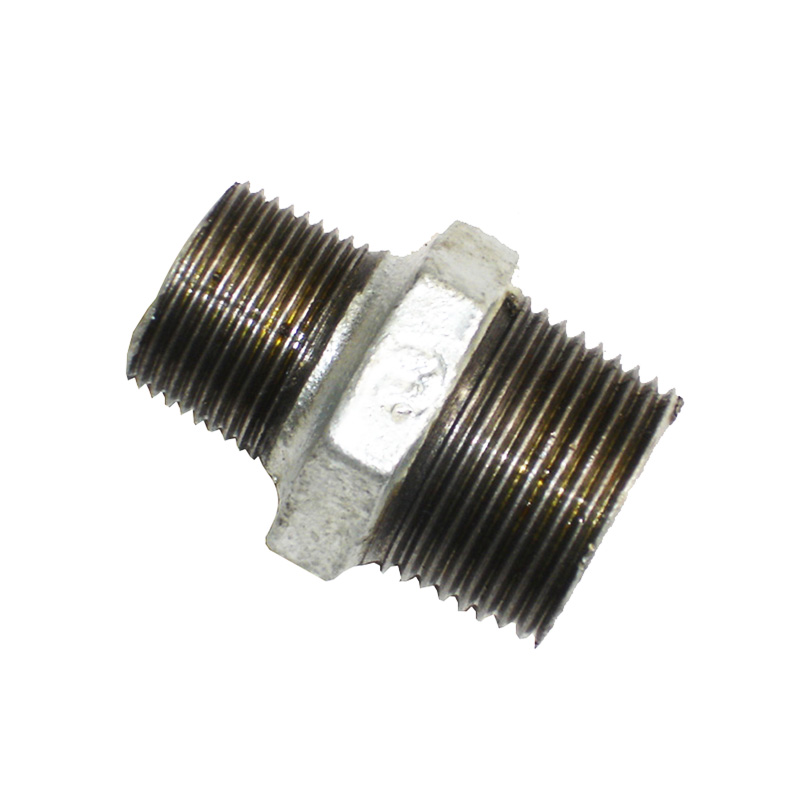
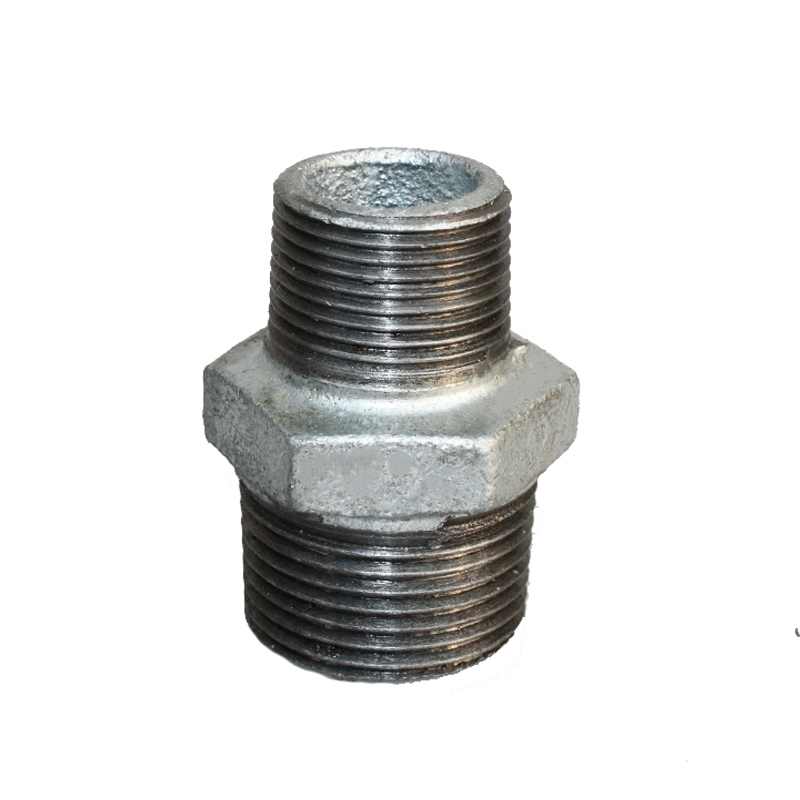
reducing nipple for sale
Maximum Pressure: 25 BAR (363PSI) (2.5MPA) CLASS 150
Maximum Temperature: 200°C (392°F)
Tensile Strength: 350MPA
Hardness: HB150 (Brinell)
Elongation Rate: 10%
Suitable Applications: Water, Oil, Gas, Petro-Chemical
Material: Malleable Iron
Do you know?
There is a 0.5 degree change in the axis angle between BSPT (BS EN 10226) and Jianzhi, but only a 0.3 degree change in the axis angle between Jianzhi and BSPT.
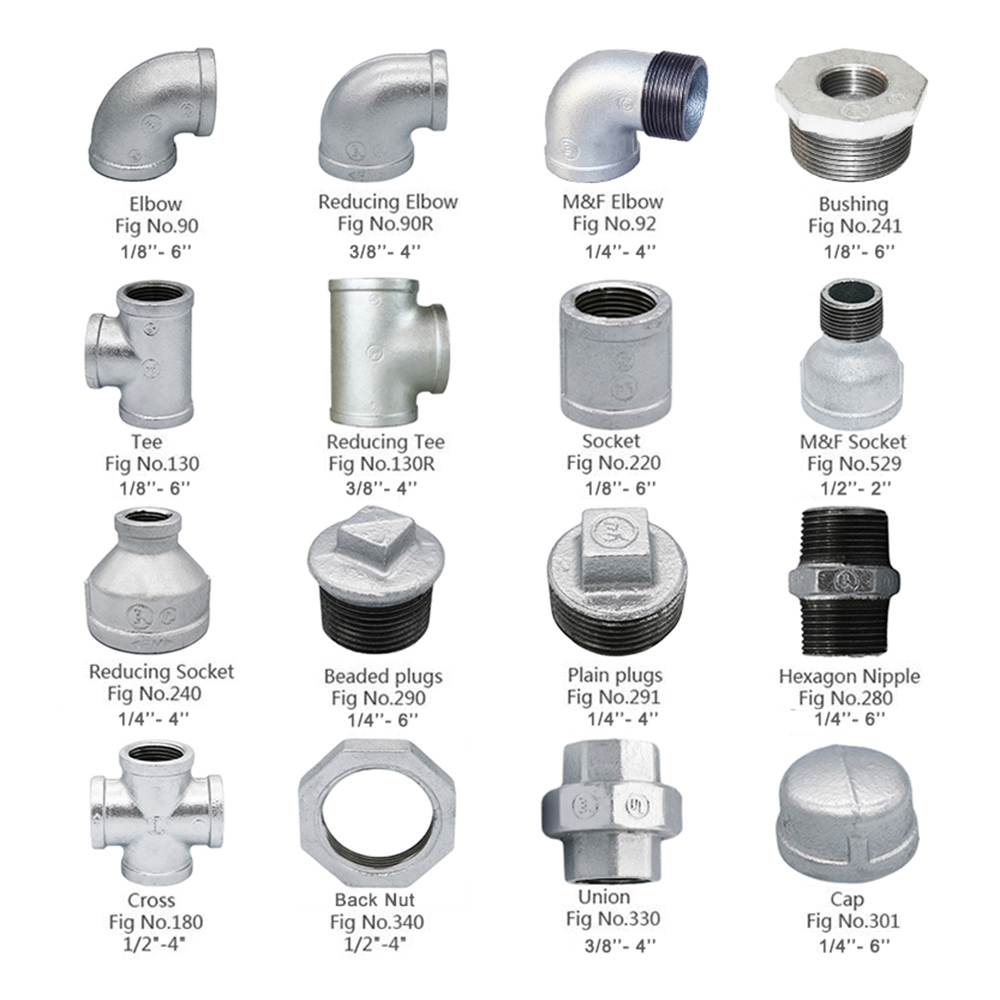
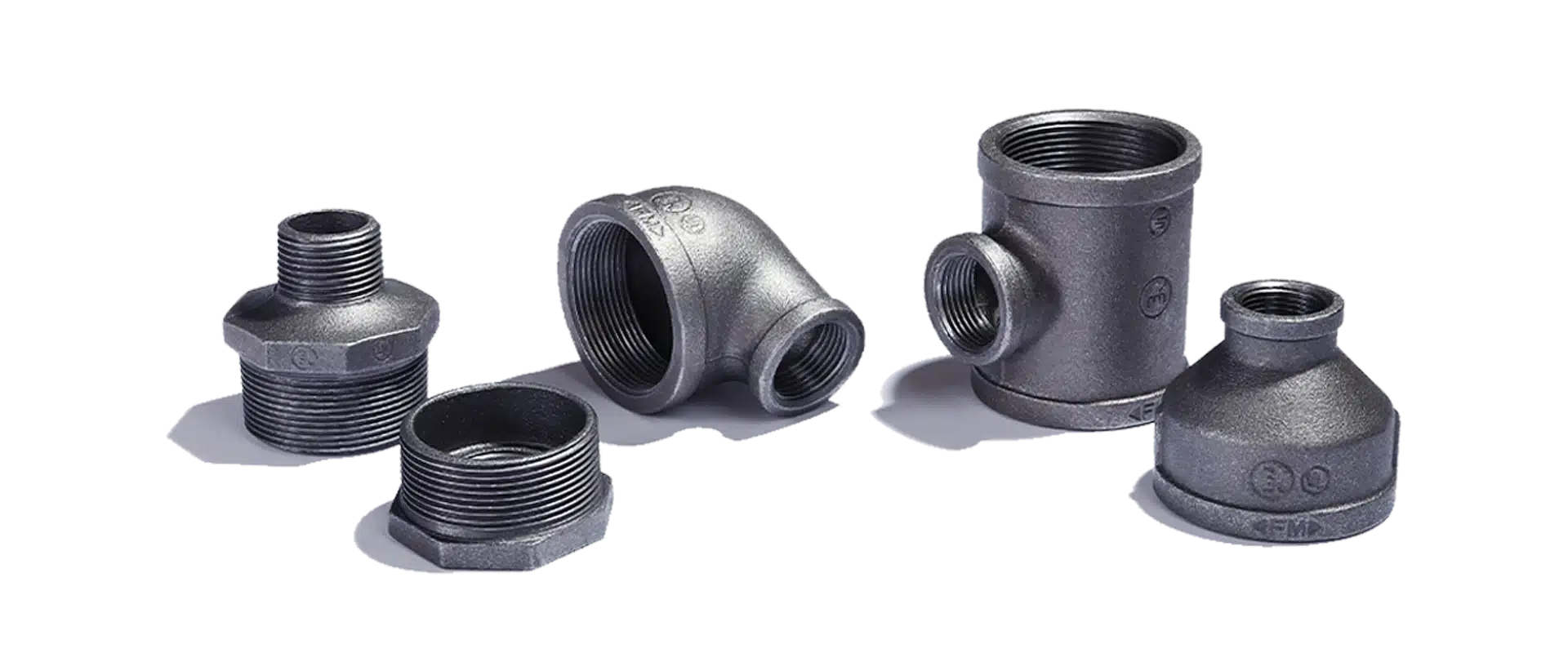
Suitable for water and gas environments, cast iron and steel fittings provide a strong and reliable connection. Cast iron and steel fittings provide a strong and reliable metal connection. These fittings can be found in a variety of forms, such as couplings, transitional couplings, locks, crosses, elbows, tees, butts, American women, and nipples, among others. Cast iron and steel fittings are used for different purposes, both outside and indoors, depending on the humidity and temperature. A chemical process known as galvanizing is used to protect products made from steel and iron (fittings) against mechanical damage. Zinc is also almost completely protected from metal oxidation (rust) when applied by hot or galvanized galvanizing.
Reducing Nipples
JANZHI-Malleable iron pipe fittings
EN10226 /ASMEB1.20.1/IS0228/IS07-1

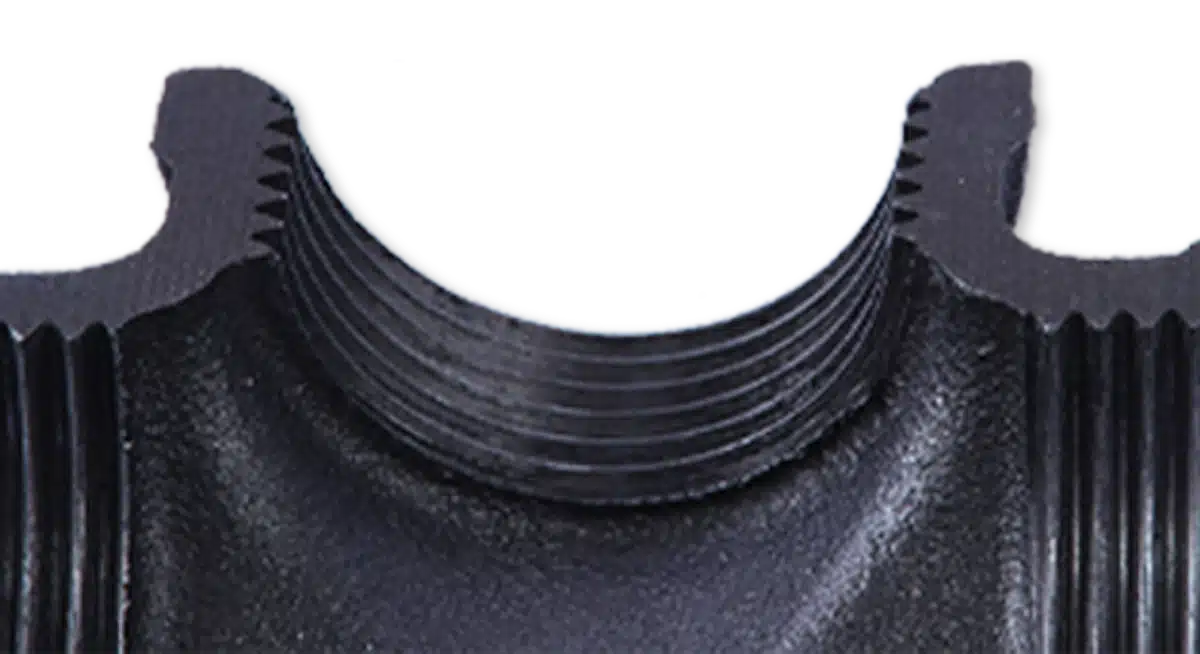
Protect pipe fittings from injury during connection

disrupting their original performance
please contact our staff


0.6MPa

standard
0.5MPa
±0.3°

standard
+0.5°
363MPa

standard
330MPa
12%

standard
8%

100% individuoltesting ofthe product

Reduce carbon emissions and
use renewable energy
Focuson sustainable development
Start from 1982
Sam floot space
Tons of production per year
Tons nbentory



|
Galvanization – Threading – Detail processing – Grinding
government group

government group
Sold to over 30
countries and regions




JANZHI Group holds 13.6% market share
Gas Pipeline System holds 60% market share
customized needs of different customers







after-sales service and technical support
Customer Service




















